D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router
ABOUT D-Link
D-Link is a global networking equipment manufacturer that provides a wide range of products and solutions for both consumer and business markets. The company was founded in 1986 and is headquartered in Taiwan. D-Link specializes in the design, development, and manufacturing of networking and connectivity devices such as routers, switches, wireless access points, network adapters, surveillance cameras, and storage solutions.
D-Link offers networking solutions for various environments, including homes, small and medium-sized businesses, and large enterprises. Their products are designed to enable seamless and reliable connectivity, whether it’s for wired or wireless networks.
In the consumer market, D-Link provides routers, Wi-Fi extenders, and smart home devices that allow users to connect and control their home networks, smart appliances, and security systems. D-Link’s consumer products often feature user-friendly interfaces and advanced features such as parental controls and Quality of Service (QoS) settings.
Package Contents
- N300 Wi-Fi Router
- Power Adapter
- Quick Install Guide
Note:
Using a power supply with a different voltage rating than the one included with the GO-RT-N300 Router will cause damage and void the warranty for this product.
System Requirements

Features
Connectivity
- 10/100 Internet port to connect to broadband Internet with high transfer speeds
- Four 10/100 LAN ports to connect wired devices for high-speed online activities
- Latest Wireless N technology for increased speed and range, plus Repeater Mode to extend the reach of your existing wireless network
Security
- NAT Firewall to control traffic and prevent exploits and intrusions
- Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) to quickly and securely add devices to your network
- WPA/WPA2 encryption to secure your wireless traffic
Ease of Use
- Web browser-based setup and configuration
- D-link n300 setup wizard download to guide you through the configuration process
* Maximum wireless signal rate derived from IEEE Standard 802.11g and 802.11n specifications. Actual data throughput will vary. Network conditions and environmental factors, including volume of network traffic, building materials, and construction, and network overhead, lower actual data throughput rate. Environmental conditions will adversely affect the wireless signal range.
Hardware Overview
Back

- LAN Ports (1-4)
Connect Ethernet devices such as computers, switches, and game consoles. - Internet Port
Connect your broadband modem to this port using an Ethernet cable. - Reset Button
Press and hold the reset button with a paper clip for six seconds to reset the router to the factory default settings. - Power Button
Press to power the router on and off. - Power Port
Connect the supplied power adapter. - WPS Button
Press to start the WPS process. The Internet LED will start to blink.
LEDs

- Power LED
A solid green light indicates a proper connection to the power supply. - Internet LED
A solid green light indicates a connection to the Internet port. The LED will blink during boot-up and
during the WPS process.
Installation
This section will walk you through the installation process. The placement of the router is very important. Do not place the router in an enclosed area such as a closet, cabinet, or in attic or garage.
Before you Begin
- Users with DSL providers – If you are using a PPPoE connection, you will need your PPPoE username and password. If you do not have this information, contact your Internet provider. Do not proceed until you have this information.
- Users with Cable providers – Make sure you unplug the power to your modem. In some cases, you may need to turn it off for up to five minutes.
- Advanced Users – If your ISP provided you with a modem/router combo, you will need to set it to “bridge” mode so the GO-RT-N300 router can work properly. Please contact your ISP or refer to the user manual for your modem/router device.
Wireless Installation Considerations
The D-Link wireless router allows you to access your network using a wireless connection from virtually anywhere within the operating range of your wireless network. Keep in mind, however, that the number, thickness, and location of walls, ceilings, or other objects that the wireless signals must pass through, may limit the range. Typical ranges vary depending on the types of materials and background RF (radio frequency) noise in your home or business. The key to maximizing wireless range is to follow these basic guidelines:
- Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the D-Link router and other network devices to a minimum -each wall or ceiling can reduce your adapter’s range from 3-90 feet (1-30 meters.) Position your devices so that the number of walls or ceilings is minimized.
- Be aware of the direct line between network devices. A wall that is 1.5 feet thick (.5 meters), at a
45-degree angle appears to be almost 3 feet (1 meter) thick. At a 2-degree angle, it looks over 42 feet (14 meters) thick! Position devices so that the signal will travel straight through a wall or ceiling (instead of at an angle) for better reception. - Building Materials make a difference. A solid metal door or aluminum studs may have a negative effect on range. Try to position access points, wireless routers, and computers so that the signal passes through drywall or open doorways. Materials and objects such as glass, steel, metal, walls with insulation, water (fish tanks), mirrors, file cabinets, brick, and concrete will degrade your wireless signal.
- Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 meters) from electrical devices or appliances that generate RF noise.
- If you are using 2.4GHz cordless phones or X-10 (wireless products such as ceiling fans, lights, and home security systems), your wireless connection may degrade dramatically or drop completely. Make sure your 2.4GHz phone base is as far away from your wireless devices as possible. The base transmits a signal even if the phone in not in use.
Manual Setup
For best results, place the router in an open area of your intended work area for better wireless coverage. Please use the computer that you are currently connecting to the Internet with.
- Unplug the power from your modem.

- Connect an Ethernet cable from the Internet port of the router to the Ethernet port on your modem.

- Connect another Ethernet cable from the Ethernet port on your computer to one of the LAN ports on the router. You can also connect wirelessly to the router with your computer. Complete steps 4 and 5 before attempting to connect.
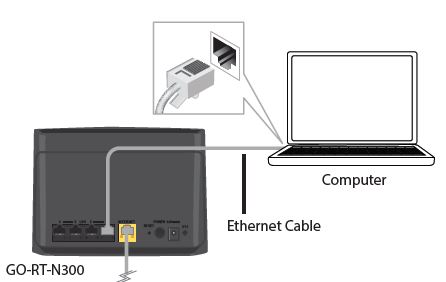
- Connect another Ethernet cable from the Ethernet port on your computer to one of the LAN ports on the router. You can also connect wirelessly to the router with your computer. Complete steps 4 and 5 before attempting to connect.

- Plug the power adapter into your router and connect to an available power outlet or surge protector. If the Power LED does not light up, press the Power button on the back of the router. If connecting wirelessly, open your wireless utility on your computer and connect to the router. The Wi-Fi network (SSID) is GO-RT-N300 Router with no password or with d’link n300 default wifi password.
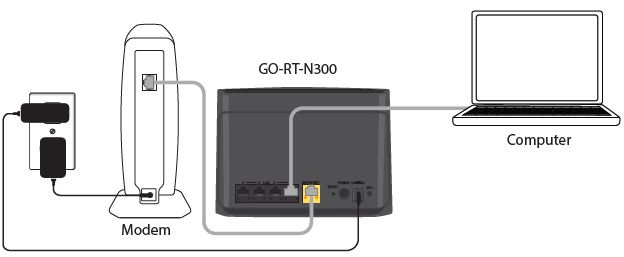
- After the router has powered up, verify that the Power and Internet LEDs are both lit. Proceed with router configuration.
Configuration
There are a couple of different ways you can configure your router to connect to the Internet and connect to your clients:
- D-link n300 setup Wizard Download – This wizard will launch if you log into the router for the first time. See below.
- Manual Setup – Log into the router and manually configure your router (advanced users only). Refer to page 15.
Setup Wizard
Open a web browser (e.g., Internet Explorer, Chrome, Firefox, or Safari) and enter the IP address of the router (192.168.0.1) or enter http://dlinkrouter.local.

Select your Internet type from the drop-down menu: DHCP (dynamic) is most commonly used with cable Internet, PPPoE (common with DSL), or Static.
If you selected DSL (PPPoE), enter your PPPoE user name and password supplied by your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
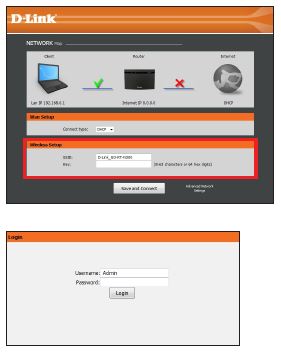
If you selected Static IP, enter the IP information and DNS settings supplied by your ISP.
At the bottom, enter the name you want for your wireless network (SSID) and then enter a d’link n300 default wifi password (Key). Click Save and Connect.

Log in to the router. The user name is Admin and leave the d’link n300 default wifi password box empty. Click Login.
The Status screen will appear. This will display your router’s current status, including LAN IP settings, wireless (WLAN) settings, and Internet (WAN) settings.

The next section will walk through the configuration utility.
Web-based Configuration Utility
Open a web browser (e.g., Internet Explorer, Chrome, Firefox, or Safari) and enter the IP address of the router (192.168.0.1) or enter http://dlinkrouter.local.
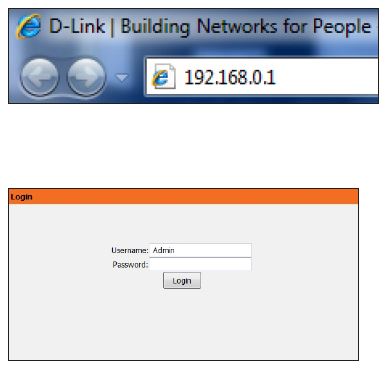
Log in to the router. The user name is Admin and leaves the d’link n300 default wifi password box empty. Click Login.
Setup Wizard
If you would like to run the setup wizard, click Next; then follow the steps below.
You can click Manual which will take you to the Setup > Internet Setup page.

- Select your Internet type and then click Next. Dynamic IP (DHCP) is most commonly used with cable Internet, PPPoE (common with DSL), or Static.
If you select Dynamic IP, skip to step 2 on the next page.
- A. If you selected DSL (PPPoE), enter your PPPoE user name and password supplied by your ISP (Internet Service Provider) and then click Next.
- B. If you selected Static IP, enter the IP information and DNS settings supplied by your ISP and then click Next.

- Select your wireless settings for the router:
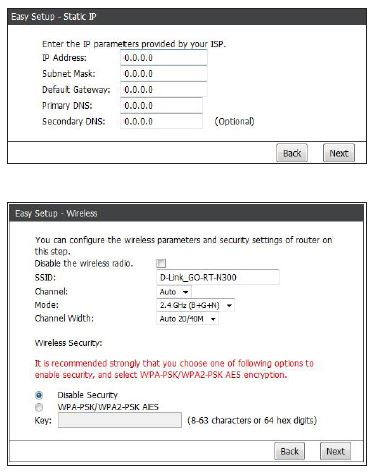
- Click Finish to complete your setup.
Local Network
This section will allow you to change the local network settings of the router and to configure the DHCP settings.

IP Address:
Enter the IP address of the router. The default IP address is
192.168.0.1.
If you change the IP address, once you click Apply Changes,
you will need to enter the new IP address in your browser to
get back into the configuration utility.
Subnet Mask:
Enter a Subnet Mask. The default is 255.255.255.0.
Apply Changes:
Click to save your settings.
DHCP Server Settings
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Control Protocol. The DHCP Server (built-in to the router) will automatically assign an IP address to the computers and devices on your network. Be sure to set your computers to be DHCP clients by setting their TCP/IP settings to “Obtain an IP Address Automatically.” When you turn your computers on, they will automatically load the proper TCP/IP settings provided by the Go-RT-N300. The DHCP Server will automatically allocate an unused IP address from the IP address pool to the requesting computer. You must specify the starting and ending address of the IP address pool.
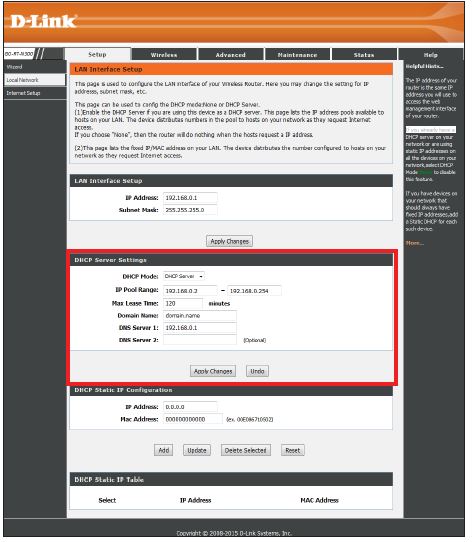
DHCP Server Mode:
Select DHCP Server to have the router automatically assign the IP settings to your computers and devices (on by default), or select None to turn DHCP off.
IP Pool Range:
Enter the starting and ending IP addresses for the DHCP server’s IP assignment.
Note:
If you statically (manually) assign IP addresses to your computers or devices, make sure the IP addresses are outside of this range or you may have an IP conflict.
Max Lease Time:
The length of time for the IP address lease. Enter the lease time in minutes (default setting is 120).
Domain Name:
Enter a domain name (optional)
DNS Server 1:
Enter a specific primary DNS server IP that you want on your devices. Leave blank to use the router’s default (from your ISP).
DNS Server 2:
Enter a specific secondary DNS server IP that you want on your devices. Leave blank to use the router’s default (from your ISP).
DHCP Static IP Configuration
If you want a computer or device to always have the same IP address assigned, you can create a Static IP (known as DHCP Reservation). The router will assign the IP address only to that computer or device. Note that this IP address must be within the DHCP IP Address Range.

IP Address:
Enter the IP address you want to assign to the computer or device. This IP Address must be within the DHCP IP pool range.
MAC Address:
Enter the MAC address of the computer or device.
Add:
Click to save your entry.
Update:
Click to refresh the DHCP Static IP Table.
Delete Selected:
Select a device from the DHCP Static Table and click to remove it.
Reset:
Click to delete all entries.
Internet Setup
Static (assigned by ISP)
Select Static IP Address if all WAN IP information is provided to you by your ISP. You will need to enter in the IP address, subnet mask, gateway address, and DNS address(es) provided to you by your ISP. Each IP address entered in the fields must be in the appropriate IP form, which are four octets separated by a dot (x.x.x.x). The router will not accept the IP address if it is not in this format.
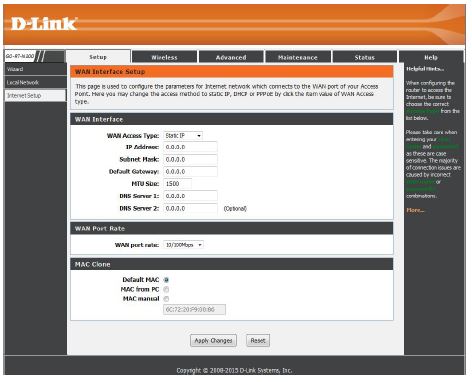
IP Address:
Enter the IP address assigned by your ISP.
Subnet Mask:
Enter the Subnet Mask assigned by your ISP.
Default:
Enter the Gateway assigned by your ISP.
Gateway MTU Size:
Maximum Transmission Unit – you may need to change the MTU for optimal performance with your specific ISP. 1492 is the default MTU.
DNS Server 1:
Enter the Primary DNS server IP address assigned by your ISP.
DNS Server 2:
Enter the Secondary DNS server IP address. This is optional.
WAN port rate:
Select the Internet port speed from the drop-down menu.
Default MAC:
Select to use the default MAC address assigned to the Internet port on your router.
MAC from PC:
Select to copy the MAC address from the computer you are currently on now to the router.
MAC manual:
Select to manually enter a MAC address to your router.
Apply Changes:
Click to save your settings.
Dynamic
Select DHCP Client to obtain IP Address information automatically from your ISP. Select this option if your ISP did not give you any IP settings to use. This option is most commonly used for cable modem services and some DSL services.

Host Name:
The Host Name is optional but may be required by some ISPs. The default hostname is the device name of the router and may be changed.
MTU Size:
Maximum Transmission Unit – you may need to change the MTU for optimal performance with your specific ISP. 1492 is the default MTU.
Attain DNS Automatically:
Select if you automatically receive the DNS server(s) from your ISP (enabled by default).
Set DNS Manually:
If you want to enter your own DNS server IP addresses, select this and enter the IP address(es) in the DNS Server 1 and 2 boxes.
WAN port rate:
Select the Internet port speed from the drop-down menu.
Default MAC:
Select to use the default MAC address assigned to the Internet port on your router.
MAC from PC:
Select to copy the MAC address from the computer you are currently on now to the router.
MAC manual:
Select to manually enter a MAC address to your router.
Apply Changes:
Click to save your settings.
PPPoE
Select PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) if your ISP uses a PPPoE connection. Your ISP will provide you with a username and password. This option is typically used for DSL services. Make sure to remove your PPPoE software from your computer. The software is no longer needed and will not work through a router.
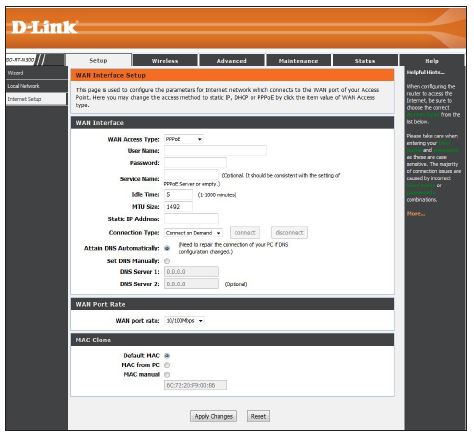
User Name:
Enter your PPPoE user name.
Password:
Enter your PPPoE password.
Service Name:
Enter the ISP Service Name (optional).
Idle Time:
Enter a maximum idle time during which the Internet connection is maintained during inactivity. This option is only available if Connection Type is set to ‘Connect on Demand’.
MTU Size:
Maximum Transmission Unit – you may need to change the MTU for optimal performance with your specific ISP. 1492 is the default MTU.
Static IP Address:
Enter the static IP address only if assigned by your ISP.
Connection Type:
Select Continuous (most common) to have the router constantly connected to your ISP, Connect on Demand to have the router connect to the Internet when you initialize a connection, or Manual if you want to manually connect/disconnect to the Internet.
Attain DNS Automatically:
Select if you automatically receive the DNS server(s) from your ISP (enabled by default).
Set DNS Manually:
If you want to enter your own DNS server IP addresses, select this and enter the IP address(es) in the DNS Server 1 and 2 boxes.
WAN port rate:
Select the Internet port speed from the drop-down menu.
FAQ’S About D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router
Q: Can I use the D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router to extend my existing Wi-Fi network?
A: The D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router may not have a built-in repeater or extender functionality. However, you can connect it to your existing network as an additional access point by configuring it in the appropriate mode or by using it as a wired switch.
Q: Does the D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router support parental controls?
A: The availability of parental control features may vary depending on the specific model within the N300 series. Some D-Link routers offer parental control settings that allow you to restrict or monitor internet access for certain devices or users, helping you manage online content and limit access for children.
Q: Can I use the D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router with my existing internet service provider?
A: Yes, the D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router is generally compatible with most internet service providers (ISPs). It should work with any broadband connection, such as cable, DSL, or fiber, as long as you configure it with the appropriate settings provided by your ISP.
Q: Does the D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router have USB ports?
A: The D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router may not have built-in USB ports. However, some models within the N300 series or higher-end D-Link routers may offer USB ports for connecting external storage devices or printers.
Q: How many devices can the D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router support simultaneously?
A: The D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router can support multiple devices simultaneously. However, the exact number of devices that can be connected and maintain optimal performance may vary based on factors such as network activity, bandwidth usage, and the capabilities of the connected devices.
Q: What is the maximum wireless speed supported by the D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router?
A: The D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router supports wireless speeds of up to 300 Mbps, which is the theoretical maximum speed achievable under ideal conditions. However, actual speeds may vary depending on factors such as distance, interference, and the capabilities of connected devices.
Q: What wireless standards does the D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router support?
A: The D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router supports the 802.11n wireless standard, which provides faster speeds and better coverage compared to older standards like 802.11g or 802.11b.
Q: What is D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router?
A: The D-Link N300 Wi-Fi Router is a wireless router manufactured by D-Link. It is designed to provide wireless internet connectivity for home or small office environments.
For more manuals by Epson visit ManualsDock
[embeddoc url=”https://manualsdock.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/D-Link-N300-Wi-Fi-Router-User-Manual.pdf” download=”all”]


