
Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4
About Altice Labs
Delivering key telecommunications technologies since 1950, Altice Labs has been shaping the future of technology, enabling Communications Service Providers and Enterprises to offer advanced and differentiated services to their customers and users.
Altice Labs is an innovation and transformation catalyst supported by a strong and dynamic Innovation Ecosystem. Through technology, we are committed to improving people’s lives and the way in which companies do business.
Technical Description
Fiber Gateway Main Functionalities
The Fiber Gateway is aimed at customer premises and complies with the ITU-T G.984.x recommendation in order to transport (over GPON) and deliver (to the premises domain) the full broadband service pack. Broadband service applications are commonly referred to as below:
- High-speed internet (HSI);
- Voice (VoIP) services (SIP/MEGACO H.248);
- TV (IPTV);
- Wi-Fi.
The multiple environments is thus reinforced when combining the upper referred services.
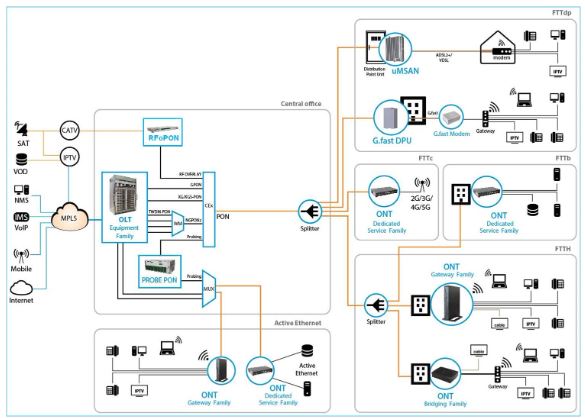
Fiber Gateway Application Scenario
The next figure shows a possible gateway scenario for Fiber Gateway equipment when in an FTTx architecture.
Interoperability
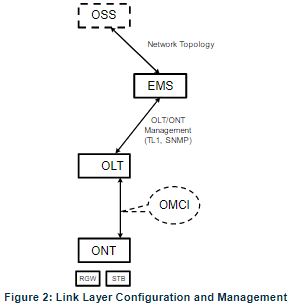
Fiber Gateway equipment complies with ITU-T G.984.x. recommendation as like G.984.4 (OMCI) ensuring multi-vendor OLT interoperability with major GPON OLT vendors, as defined in BBF.247 ONU certification program. BBF.247 ONU certification program certifies ONT link layer configuration and management protocol, OMCI, Figure 2, as defined by ITU-T G.984.3, ITU-T G.984.4, and ITU-T G.988.
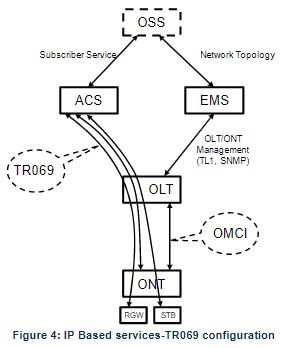
IP-based services configuration and management are achieved by means of the TR-069 protocol as defined by Broadband Forum. This procedure takes for granted that previously the link layer connectivity has been achieved. TR-069 is then transparent to the OLT since the TR-069 connections are established between the ACS and the ONTs, Figure 4.
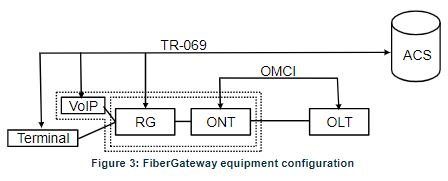
ONT gateway family equipment integrates gateway functionalities. Link layer configuration and management is achieved by the use of OMCI, while IP-based services (RG functionality and Voice over IP) are configured and managed by TR-069, Figure 3.
Interfaces
Client interface options are of types:
- 4x 10/100/1000Base-T for Ethernet network connection (RJ45 connectors);
- 2x FXS channels (RJ11 connectors);
- Wi-Fi:
- MIMO 4×4 @ 2.4GHz wireless interfaces (802.11 b/g/n);
- MIMO 4×4 @ 5 GHz wireless interfaces (802.11 a/n/ac);
- 1x USB 2.0 Master for printer sharing, media sharing, and for 3G/4G backup uplink;
- Control switches for power and Wi-Fi;
The network interface option is of type:
- GPON SC/APC Optical connector (B+/C+).
General Features
GPON is a point-to-multipoint passive optical network, in which unpowered optical splitters are used to enable a single optical fiber to serve multiple premises, typically 1-64.
A PON consists of an optical line terminal (OLT) at the central office and a number of optical network terminals (ONT) at the customer premises. Downstream signals are broadcasted to all premises sharing multiple fibers. Encryption can prevent eavesdropping.
Upstream signals are combined using a multiple access protocol (Time Division Multiple Access – TDMA). The OLT queues data to the various ONT terminals in order to provide time slot assignments for upstream communication. In Figure 5 it is shown a scenario for a multi-service user domain basic architecture through an ISP network.
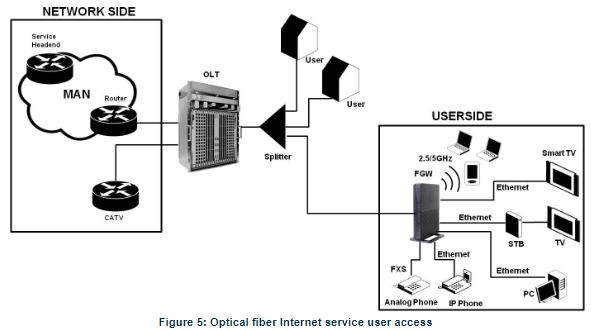
In the upstream direction, the Fiber Gateway is connected to the optical splitter and respectively to the OLT through the PON port to provide integrated access services through the service headend. In the downstream direction, the Fiber Gateway is connected to various terminals through the following LAN-side ports to implement multi-play services:
- Four 10/100/1000M Base-T Ethernet ports, which can be connected to terminals such as PCs, STBs, and video phones to provide high-speed data and video services;
- Two FXS ports, which can be connected to telephone sets to provide VoIP services;
- Four Wi-Fi antennas, which can connect to Wi-Fi terminals wirelessly to provide a secure and reliable high-speed wireless network;
- One USB port, which can be connected to a USB storage device to provide convenient storage and file-sharing services within a home network;
The communication between client equipment (ONT) and the ISP access routers (MAN edge) is made by an optical fiber-based passive architecture (ITU-T G.984 Recommendation). The GPON network acts as a Layer 2 Ethernet metropolitan network. Access network assures and controls the media (MAC) communication through a TDMA scheme, introducing GEM (GPON Encapsulation Method) in between to adapt the TDM layer to Ethernet. The used protocol stack is shown in Figure 6.
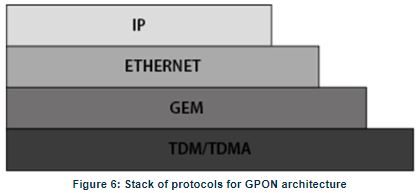
Several transmission containers (T-CONT) are assigned to each user. Each T-CONT has an associated GEM port and each GEM port has a VLAN identifier and an 802.1p priority level. The ONT classifies the traffic depending on the VLAN and the marked priority and routes it over the corresponding T-CONT/GEM port. Thus for frame multiplexing, GEM and T-CONT ports are used for uplink while the downlink only uses the GEM ports feature.
Fiber Gateway complies with Broadband Forum TR-142 Technical Report, which defines a framework for the remote configuration and management of IP-based services over PON (Passive Optical Network) and fiber access technology. TR-142 framework uses TR-069 which is the protocol of choice for the remote management and configuration of IP services over PON and fiber access networks. TR-069 is intended to be used for the remote configuration and management of IP services running over ONT, as well as for some aspects of ONT management.

TR-142 framework defines a virtual UNI between the OMCI (ONT Management Control Interface) and TR-069 management domains. This framework allows PON CPE with L3 layer capabilities to be mass remotely configured, troubleshoot, and managed by an ACS (Auto Configuration Server) using TR-069 CPE WAN Management Protocol.
General Architecture
Fiber Gateway basic system architecture is hereafter presented.
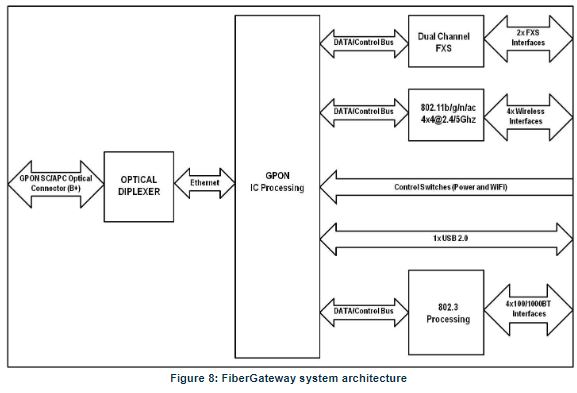
The GPON IC Processing unit is the core component inside FiberGateway. It is responsible for the interconnection and processing between client-side interfacing and the optical GPON Uplink interface.
GPON
The Fiber Gateway GPON layer as G.984.x uses 1490nm downstream and 1310nm upstream of the optical wavelength, with 2,488Gbps downstream and 1,244Gbps upstream by using an SC/APC protected optical connector.
Ethernet
Ethernet is the wired LAN technology and is revised in the IEEE 802.3 standard. At the OSI reference system, Ethernet is at the Data Link layer. In the Fiber Gateway equipment, both WAN and LAN type of physical interfaces are 10/100/1000BASE-T AUTO-MIX Ethernet type over RJ45 connectors.
IPTV
For the IPTV service, the Fiber Gateway also behaves like a Layer 2 bridging device. For this service, the Fiber Gateway has a specific GEM PORT for Multicast. This same GEM PORT is requested by the user in order to have access to the various IPTV channels. Every time a user requests a new channel, the Fiber Gateway will send OLT an IGMP packet requesting that Channel. The Fiber Gateway is also responsible for implementing snooping for the channels that the user requests.
Voice
Supported VoIP specifications
- Call control: SIPv1/v2;
- T.38 Fax relay;
- Fax/Data bypass;
- Echo canceller;
- Echo canceller length;
- Jitter buffer;
- Caller ID generation;
- G.711 PCMU;
- G.711 PCMA;
- G.723.1;
- G.726;
- G.729;
- VAD and CNG;
- Caller ID and call waiting;
- RTP/RTCP packet encapsulation;
- RFC 2833 Support;
- In-band signaling detection and generation (DTMF, call progress tones).
- Automatic Tone generation (dial, busy, ring back, stutter, distinctive ring);
- 3-Way conferencing.
Supported interfaces
FiberGateway voice service provisioning could be made through OLT configurations over OMCI messages or could be downloaded (FTP) from the OLT up to the FiberGateway after its registration on the PON network. FiberGateway equipment have the ability to deliver Voice service over two types of interface:
Logical interface (VLAN encapsulation)
If the FiberGateway has no FXS ports and the VoIP service is transparently forwarded from the OLT up to the Home Gateway (and vice versa) within a previously defined voice VLAN. FiberGateway respects the defined priority and implements the traffic encapsulation from its own Ethernet interface into a specific T-CONT/GEM-Port over the PON interface and up to the OLT equipment.
Physical interface (FXS ports)
The FiberGateway has physical RJ11 FXS interfaces. In this version of the FiberGateway equipment, voice interfaces are terminated in the equipment by means of FXS (RJ11) connections. The RJ11 analog terminals adapter function is auto/self-configured, integrated (analog/VoIP), and associated with a defined SIP or Megaco (H.248) user.
The FiberGateway will allow VoIP or NGN (Next Generation Network) traffic from devices connected to the RJ11 or RJ45 interfaces, towards the same internal VLAN.
Apart from the SIP and Megaco (H.248) self-configuration, it is also possible to make modifications in the voice service configurations by updating the FiberGateway SW through download from the OLT via OMCI. The FiberGateway equipment has a DHCP client to get an IP address, alternatively, the FiberGateway could be configured with a static IP. The configuration of the static IP or DHCP client is related to the WAN side and is enabled by the OLT.
Wi-Fi
FiberGateway Block Diagram
The FiberGateway circuit block diagram is presented in the figure below showing all oscillators in the device and their frequencies, Figure 9. Intentional radiators in the circuit and radio signal path between circuit blocks are also shown.

Operational Description
The FiberGateway supports Wi-Fi, with Wi-Fi interfaces operating in the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies
The FiberGateway complies with the following standards:
- IEEE 802.11a (5GHz, up to 54 Mbps)
- IEEE 802.11b (2.4GHz, up to 11 Mbps)
- IEEE 802.11g (2.4GHz, up to 54 Mbps)
- IEEE 802.11n (2.4GHz and 5 GHz, up to 600 Mbps)
- IEEE 802.11ac (5GHz, up to 1733 Mbps)
The ONT supports the following features:
- wireless security
- WEP encryption (64/128 bits)
- WPA (Wireless Protect Access) TKIP
- WPA2 AES
- WPA2 mixed
- 802.1x Authentication
- External RADIUS Authentication
- Client access control through media access control (MAC) filter
- Dynamic cryptography (TKIP and AES)
- Multiple SSIDs Profiles
- WPS (Pushbutton and PIN entry);
Interfaces and features
- Dual-band, concurrent mode 2.4GHz plus 5GHz via internal Wi-Fi antennas,
- Compliant with IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac and with 4×4 MIMO
- Up to 34dBm EIRP both in the 2.4GHz and in the 5GHz
- Channel Bandwidth: 20, 40, 80, 80+80, 160
- Support of zero wait for dynamic frequency selection (DFS): 4×4 with weather radar detection
- Multi-User MIMO for better performance per user
Data Rates
- 802.11a : 6,9,12,18,24,36,48,54 Mbps
- 802.11b: 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps
- 802.11g: 6,9,12,18,24,36,48,54 Mbps
- 802.11n: up to 600 Mbps
- 802.11ac: up to 1733 Mbps
- 1024QAM (2.4GHz) : up to 1000 Mbps
- 1024QAM (5GHz) : up to 2166 Mbps
Antennas
- 4×4 MIMO antennas
- Internal antennas with 4~5dBi antenna gain
Multiple QoS per VLAN
The FiberGateway supports 802.1p QoS per VLAN service in which several flows (one per allowed bit) are embedded in the same VLAN. According to the applied configuration, the FiberGateway performs a per-flow QoS policy: dropping traffic marked with not allowed bits and limiting to the configured value the data rate of the allowed flows. The FiberGateway performs transparent VLAN translation. It is transparent to upper-layer protocols, such as ARP, RIP, DHCP, IGMP, PPP, etc.
Policing/Rate Limiting
Downstream QoS
The OLT system supports traffic classification at the ingress ports (ETH, LAGs, PON, etc) based on P-Bits, IP DSCP, and IP. The OLT system provides several QoS mechanisms, that can be targeted to the flow characterized by one or two VLANs according to the type of service or can be targeted to the priority of the packet, where each p-bit/DSCP is mapped in one of eight queues of each port.
Each OLT port is associated with eight queues, for each of these queues is possible to configure the p-bit mapping in one of the queues, the scheduler type (Strict Priority or Weighted Fair Queuing), and the minimum and maximum bandwidth of each queue.
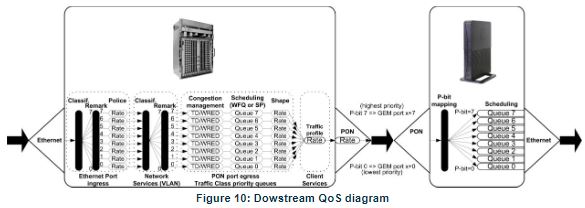
In the downstream direction, Figure 10, the ingress traffic can be first classified. It passes by a policer and is configured to each ONT service, which is defined by one or two tags. It is remarked and policed per-CoS rate (port profile). After this, Network services (per VLAN) classification determines the PON port queue where packets will wait for a transmission opportunity, and can remark the CoS (P-bits in VLAN PCP).
The traffic is put in a queue according to the p-bit/DSCP->Traffic Class mapping. Each of these Traffic Classes is associated with a scheduler (WRR or SP) and police. Queue congestion management is used to prevent the queue from overflowing and is performed based on Tail Drop or WRED. Each queue is served by either a priority or weighted scheduler and rate controlled. Then Traffic Classes to P-bit remarking are done and the traffic flows to the GPON interface.
Destination ONU/ONT client service downstream profile defines traffic classless policing. The overall PON port may be limited to a percentage of its capacity. Traffic arriving to the ONU/ONT it will pass by a mapping block which will map the traffic in one of the eight queues according to the p-bits; these queues have a Strict Priority scheduler in order to guarantee that the most prioritized traffic passes first, Figure 10.
Upstream QoS

In the upstream, Figure 11, for each T-CONT DBA the ingress traffic in the ONT passes by a mapping block that maps the traffic in one of the eight queues according to the p-bit, (in case the ingress traffic is untagged a DSCP->p-bit mapping is performed). These queues have a Strict Priority Scheduler. Packets are stored at the intended T-CONT priority queue, which is scheduled according to ONT configuration.
The ONT “waits” until the OLT assigns a transmission timeslot for that T-CONT, according to DBA, so that the most prioritized queues are the ones that transmit first. In the OLT PON ingress port, traffic is remarked and can be policed per CoS. The traffic is put into a Traffic Class according to what is defined in the p-bit/DSCP->queue mapping. Each of these Traffic Classes has an associated scheduler and policer. Queue management is performed based on Tail Drop or WRED. Then Traffic Classes to P-bit remarking is done and the traffic is sent to the uplink, Figure 11.
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA)
The DBA (Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation) is available in order to optimize the upstream bandwidth. This mechanism consists in defining an adequate T-CONT for the service traffic in question. There are five types of T-CONT, defined by the Fixed, Assured, and Maximum Parameters:
- Type 1: Only fixed Bandwidth;
- Type 2: Only Assured Bandwidth;
- Type 3: Assured+Maximum Bandwidth;
- Type 4: Only Maximum Bandwidth (Best Effort);
- Type 5: Fixed+Assured+Maximum Bandwidth.
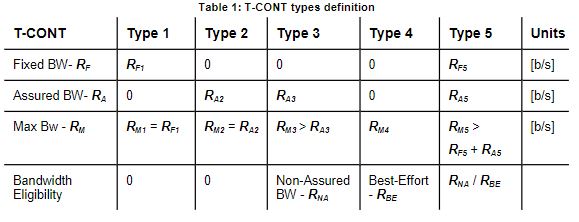
In each GPON interface there are 1024 Alloc-ID (T-CONT identifiers) available, provided to manage ONT services. They are distributed in the following way:

Upstream QoS scenarios
- 8 priority queues
- Strict-priority
- Upstream Scheduling:
- Strict Priority (currently supported)
- Strict Priority + rate controller (currently supported)
- Strict Priority + WFQ (can be SW supported)
FAQs About Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4
Q: What is Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4?
A: Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway is a router and fiber gateway device designed for use with fiber optic internet services.
Q: What are the features of Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4?
A: The Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway offers features such as Wi-Fi connectivity, Gigabit Ethernet ports, VoIP support, and advanced security protocols.
Q: How many devices can be connected to the Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 at once?
A: The Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway supports up to 253 devices connected at once.
Q: What type of internet connection does Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 support?
A: The Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway is designed for use with fiber optic internet services.
Q: What is the maximum speed that Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4x4can handle?
A: The Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway can handle internet speeds up to 1 Gbps.
Q: Does Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 support VPN connections?
A: Yes, the Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway supports VPN connections.
Q: Can Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 be used with any internet service provider?
A: The Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway may only be compatible with specific internet service providers, depending on the region.
Q: What is the warranty on Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4?
A: The warranty for the Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 may vary by region and seller. It is recommended to check with the seller or manufacturer for more information on the warranty.
Q: Can I configure Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 to work with my own router or network setup?
A: Yes, it may be possible to configure the Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4x4to work with your own router or network setup. However, it is recommended to consult the user manual or contact the manufacturer for assistance with configuration.
For more manuals by Altice Labs, Visit Manualsdock
[embeddoc url=”https://manualsdock.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Altice-Labs-FGW-GR240BG-Fiber-Gateway-4×4-User-Manual.pdf” download=”all”]
Q: What is Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4?
A: Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway is a router and fiber gateway device designed for use with fiber optic internet services.
Q: What are the features of Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4?
A: The Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway offers features such as Wi-Fi connectivity, Gigabit Ethernet ports, VoIP support, and advanced security protocols.
Q: How many devices can be connected to the Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 at once?
A: The Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway supports up to 253 devices connected at once.
Q: What type of internet connection does Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 support?
A: The Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway is designed for use with fiber optic internet services.
Q: What is the maximum speed that Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4x4can handle?
A: The Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway can handle internet speeds up to 1 Gbps.
Q: Does Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 support VPN connections?
A: Yes, the Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway supports VPN connections.
Q: Can Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 be used with any internet service provider?
A: The Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway may only be compatible with specific internet service providers, depending on the region.
Q: What is the warranty on Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4?
A: The warranty for the Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 may vary by region and seller. It is recommended to check with the seller or manufacturer for more information on the warranty.
Q: Can I configure Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4×4 to work with my own router or network setup?
A: Yes, it may be possible to configure the Altice Labs FGW-GR240BG Fiber Gateway 4x4to work with your own router or network setup. However, it is recommended to consult the user manual or contact the manufacturer for assistance with configuration.
For more manuals by Altice Labs, Visit Manualsdock


